|
This workshop is held jointly with
the Canadian conference on Computer & Robot Vision (CRV'06)
|
E
|
Editorial from Workshop Chairs
|
|
O
|
Oral Papers*
Thusday, 8 June, 2006 (15:10-17:50) - as Special Session of CRV'06
(Full papers can be downloaded from ieeexplore.ieee.org or by clicking on the paper title)
|
| 1 |

[Talk slides]
|
A Pixel-Weighting Method for Discriminating Objects of Different Sizes in an Image Captured from a Single Camera
Mookyung Park, Namsu Moon, Sang Rim Ryu, Jeong Pyo Kong, Y.J. Lee, W.J. Mun (S1 Corporation, Korea)
Abstract - A novel method of pixel-weighting is proposed to calculate the size of a detected object in an image captured using a single camera. The calculated object size does not vary significantly regardless of the location of the object in an image, which allows it to be effectively utilized in a vision-based surveillance sensing algorithm as a meaningful feature for discriminating human intruders from other objects. Experimental results show the feasibility of the proposed method.
|
| 2 |

[Talk slides] [Video]
|
A Novel Clustering-Based Method for Adaptive Background Segmentation
S. Indupalli, M.A. Ali, B. Boufama (University of Windsor)
Abstract - This paper presents a new histogram-based method for dynamic background modeling using a sequence of images extracted from video. In particular, a k-means clustering technique has been used to identify the foreground objects. Because of its shadow resistance and discriminative properties, we have used images in the HSV color space instead of the traditional RGB color space. The experimental results on real images are very encouraging as we were able to retrieve perfect backgrounds in simple scenes. In very complex scenes, the backgrounds we have obtained were very good. Furthermore, our method is very fast and could be used in real-time applications after optimization.
|
| 3 |
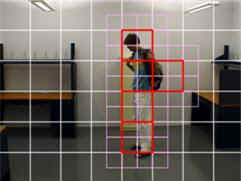 |
Object detection and tracking using iterative division and correlograms
Rafik Bourezak and Guillaume-Alexandre Bilodeau (Ecole Polytechnique de Montreal)
Abstract - This paper presents algorithms for the detection and tracking of moving objects and their relationships. The algorithms are based on color and texture analysis for real time processing. Our goal is to study human interaction by tracking people and objects for surveillance applications. The object detection algorithm is based on color histograms and iteratively divided interest regions for motion detection. The tracking algorithm is based on correlograms which combines spectral and spatial information to match detected objects in consecutive frames.
|
| 4 |
 |
Collaborative Multi-Camera Surveillance with Automated Person Detection
Trevor Ahmedali and James J. Clark (McGill University)
Abstract - This paper presents the groundwork for a distributed network of collaborating, intelligent surveillance cameras, implemented on a set of low-cost embedded microprocessor- based camera modules. Each camera trains a person detection classifier using the Winnow algorithm for unsupervised, online learning. Training examples are automatically extracted and labelled, and the classifier is then used to locate any person instances. To improve detection performance, multiple cameras with overlapping fields of view collaborate to confirm results. We present a novel, unsupervised calibration technique that allows each camera module to efficiently understand its spatial relationship with the other cameras. During runtime, cameras apply the learned spatial correlations to confirm each other’s detections. This technique implicitly handles non-overlapping regions that cannot be confirmed. Its computational efficiency makes it well-suited to real-time processing on our hardware.
|
| 5 |

[Talk slides] [Video]
|
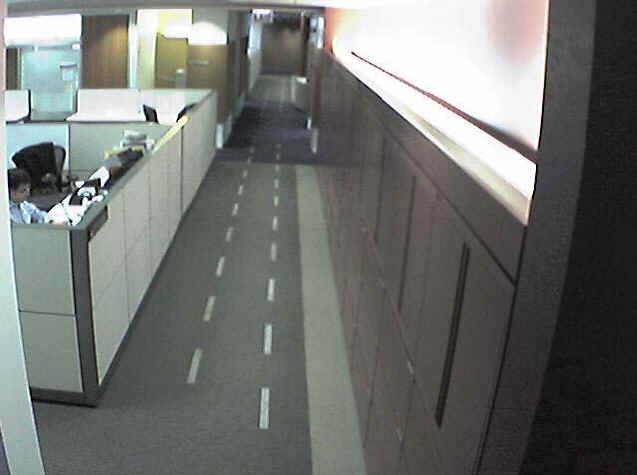
A Multiple-Sensor Indoor Surveillance System
Valery A. Petrushin, Omer Shakil, Damian Roqueiro, Gang Wei, Anatole V. Gershman (Accenture Technology)
Abstract - This paper describes an approach for people localization and tracking in an office environment using a sensor network that consists of video cameras, infrared tag readers, a fingerprint reader and a PTZ camera. The approach is based on a Bayesian framework that uses noisy, but redundant data from multiple sensor streams and incorporates it with the contextual and domain knowledge that is provided by both the physical constraints imposed by the local environment where the sensors are located and by the people that are involved in the surveillance tasks. The experimental results are presented and discussed.
|
| 6 |
[Talk slides] [Video]
|
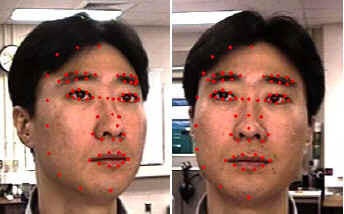
3D Face Reconstruction from Stereo Video
Unsang Park, Anil K. Jain (Michigan State University)
Abstract - Face processing in video is receiving substantial attention due to its importance in many security-related applications. A video provides rich information about a face(multiple frames and temporal coherence) that can be utilized in conjunction with 3D face models, if available, to establish a subject’s identity. We propose a 3D face modeling method based on constructing a user-specific model derived from a generic 3D face model and stereo images (two video frames) of the user. The user-specific 3D face model can be used both in enrollment and recognition stages. The advantage of utilizing reconstructed 3D face model is demonstrated by conducting face recognition experiments for 9 probe subjects against a gallery database containing 100 subjects.
|
| 7 |
 |
User Authentication based on Face Recognition with Support Vector Machines
Paolo Abeni, Madalina Baltatu, Rosalia D’Alessandro (TelecomItalia Lab, Italy)
Abstract - The present paper proposes an authentication scheme which relies on face biometrics and one-class Support Vector Machines. The proposed recognition procedures are based on both a global approach and on a combination of a global and a component- based approaches. Two different features extraction methods and three light compensation algorithms are tested. The combined system outperforms the global system and yields a significant performance enhancement with respect to the prior results obtained with the one-class Support Vector Machines approach for face recognition.
|
| P |
Poster/Demo Papers**
Friday, 9 June, 2006 (15:30-17:30) - jointly with CRV'06 poster session
(Full papers can be downloaded directly by clicking on the florafox-nnv.ru)
|
| 1 |

[Poster]
|
Region Competition for Object Tracking by Using Kullback-Leibler Distance and Level Set Contours
Mohand Saïd Allili and Djemel Ziou (Université de Sherbrooke)
Abstract - In this paper, we propose a novel object tracking algorithm in video sequences. The formulation of our tracking model is based on variational calculus, where region and boundary information cooper-ate for object boundary localization by using active contours. In the approach, only the segmentation of the objects in the 1rst frame is required for initialization. The evolution of the object contours on a current frame aims to 2nd the boundary of the objects by minimizing the Kullback- Leibler distance of the region features distribution in the vicinity of the contour to the objects versus the background respectively. We show the effectiveness of the approach on examples of object tracking performed on real video sequences.
|
| 2 |

[Poster]
|
Tracking Multiple People for Video Surveillance
M. A. Ali, S. Indupalli and B. Boufama (University of Windsor)
Abstract - This paper addresses the problem of detecting and tracking multiple moving people in a complex environment with unknown background. In this paper, we propose a new correlation-based matching technique for feature-based tracking. Our method was compared with two existing matching techniques, namely the normalized Euclidean distance and histogram-based matching. Experimental results on real-images suggest that our correlation-based approach is more accurate and efficient than the other two approaches.
|
| 3 |

[Poster]
|
Detection of Moving Objects in Video Scene - MPEG like Motion Vector vs. Optical Flow
Kunio Takaya (University of Saskatchewan)
Abstract - This paper demonstrates the use of motion vector as dened in MPEG video encoder to detect and crudely segment moving objects in video scene. The proposed motion vector search algorithm incorporated a mechanism to suppress search in the still background and to invalidate the motion vectors found at search boundaries. This paper presents four cases of video clips processed to calculate and identify the MPEG like motion vectors greater than a certain magnitude and to segment out corresponding macro-blocks, which constitute a crude segmentation of moving objects(https://florafox-ekb.ru/). The MPEG like motion vectors drawn for a consecutive image pair were compared against the vector field calculated by the optical ow method for subjective comparison.
|
| 4 |

[Poster]
|
ACE Surveillance: the next generation surveillance for long-term monitoring and activity summarization
Dmitry O. Gorodnichy (NRC-IIT)
Abstract - This paper introduces a new concept for the area of video surveillance called Critical Evidence Snapshot. We show that automatic extraction and annotation of Critical Evidence Snapshots, which are defined as video snapshots that provide a piece of information that is both useful and new, is the key to improving the utility and efficiency of video surveillance systems. An implementation of an ACE (Annotated Critical Evidence) Surveillance system made from off-the-shelf cameras and a desktop is described. The results obtained on several real-life surveillance assignments confirm our vision for ACE Surveillance as the next generation technology for collecting and managing surveillance data.
|
| 5 |

[Poster]
|
Associative tracking and recognition in video
Dmitry O. Gorodnichy (NRC-IIT)
Abstract - Due to limited resolution and quality of surveillance video, tracking and recognizing of objects in surveillance video requires techniques for accumulation of information about the object over time. The simplest of these techniques is histograms, which computes the distribution of pixel values over time and which is frequently used for tracking uniformly coloured objects such as faces. Another well-known technique for the purpose is correlograms, which learns pixel values and their spatial relationship to yield better discriminative power. However, this technique does not offer a complete learning-over-time solution either, because it updates the information about the object, which is expressed in terms of cooccurance matrices, using the currently observed pixels only and ignoring the preceding learning history. Associative neural network based memorization can thus be seen as a next-level data accumulation technique suitable for learning of objects in video over time, which takes into account both the learning history and the spatial information about the object. This presentation describes how to use the Open Source Associative Neural Network code for tracking and recognition of objects in video. Two demos showing multiple-face tracking and classification in low-resolution video are shown.
|
| 6 |
[Poster]
|
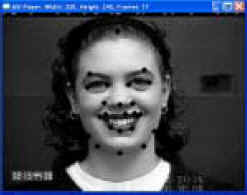
Sequence Based Face Characterization Using Factorized Feature Points.
Xiaozhou Wei and Lijun Yin (SUNY Binghamton).
Abstract - In this paper, we proposed a face tracking and reconstruction scheme for face representation, human computer interaction, and the application of security. We applied a CDOF (Color Distribution Based Optical flow) approach to track the feature points in a facial video sequence. The extracted feature points sequence are then used as an input to derive their 3D coordinates using a factorization based algorithm. In combining with our model based expression generation approach, a facial expression from a 2D input can be reconstructed as a 3D output. The feasibility, limitation and future development of the proposed scheme are discussed through the experimentation.
|
| 7 |

[Poster]
|
Video-Surveillance application with Self-Organizing Maps
Mohamed Dahmane and Jean Meunier (Université de Montréal)
Abstract - In this demo, we present an approach for video surveillance detection of abnormal events based on target trajectory analysis. The methodology follows a typical modular form: Detection/ Tracking/ Recognition. The detection step is based on the color constancy principle and uses an adaptive background subtraction technique with a shadow elimination model. The target tracking involves a direct and inverse matrix matching process. In the recognition stage we consider local motion properties (flow vectors), and more global ones expressed by elliptic Fourier descriptors. From these temporal trajectory characterizations, two Kohonen maps allow to distinguish normal behavior from abnormal or suspicious ones. The classification results show a 94.6 % correct recognition rate with video sequences taken by a low cost webcam. The system runs at a 12Hz absolute minimum video acquisition frequency, providing essentially real-time analysis.
|
| 8 |

[Poster]
|
Fall Detection Using 3D Head Trajectory Extracted From a Single Camera Video Sequence.
Caroline Rougier and Jean Meunier (Université de Montréal)
Abstract — In Western societies, the population grows old, and we must think about solutions to help them to stay at home in a secure environment. By providing a specific analysis of people behavior, computer vision offers a good solution for healthcare systems, and particularly for fall detection. This demo will show the results of a new method to detect falls using a monocular camera. The main characteristic of this method is the use of head 3D trajectories for fall detection.
|
| 9 |

[Poster]
|
Detection of Medication Intake.
Myriam Valin and Jean Meunier (Biomedical Engineering Institute, Université de Montréal)
Abstract - In the context of the growing proportion of seniors in the western world population and the efforts provided in home care services, a computer vision system has been developed for monitoring medication intake. The system can detect automatically medication intake using a single webcam. Person detection and tracking over the video sequence is done using color-based techniques while the recognition of the medication intake activity is performed using a multi-level scenario model. Experimental results in controlled conditions are shown.
|
* Oral papers are published by IEEE Computer Society Press as part of the the CRV'06 Proceedings. The BibTex reference of these papers is: @inproceedings{vp4s06-paper, title = "... ", author = "...", year="2006", booktitle = "First International Workshop on Video Processing for Security (VP4S-06) in Proceedings of Third Canadian Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV'06), June 7-9, Quebec City, Canada", pages = "" }
** Poster/Demo papers are published online at the workshop website. The BibTex reference of these papers is: @inproceedings{vp4s06-paper, title = "... ", author = "...", year="2006", booktitle = "First International Workshop on Video Processing for Security (VP4S-06), June 7-9, Quebec City, Canada (online at www.computer-vision.com/4security)}
|

















